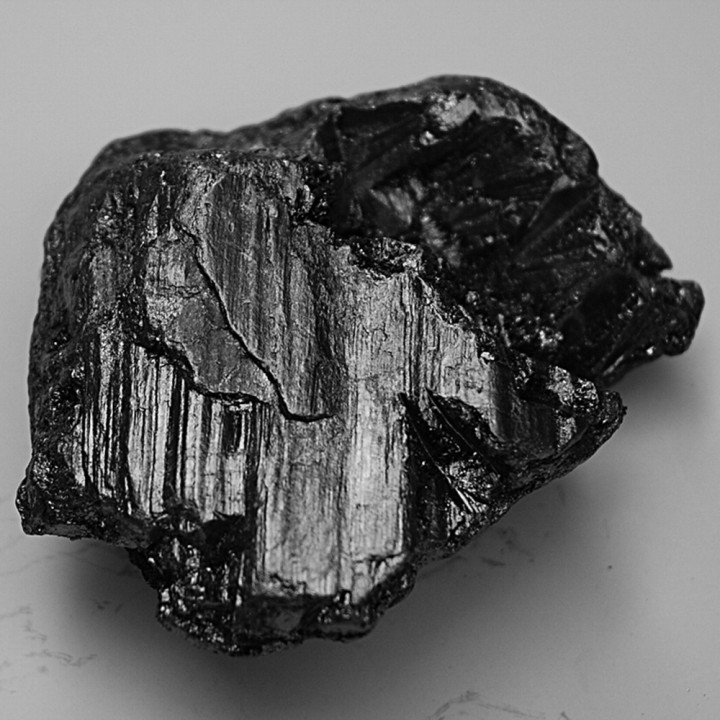
On December 18, 2024, U.S. graphite mining companies formally requested the U.S. government to impose a substantial 920% tariff on graphite imports from China. This move aims to counteract what they perceive as unfair trade practices and to bolster domestic production of this critical mineral essential for electric vehicle (EV) batteries and various electronic devices.
Background and Rationale:
- Market Dominance: China currently controls approximately 70% of global graphite production, granting it significant influence over pricing and supply chains.
- Existing Tariffs: The U.S. has a 25% tariff on most Chinese graphite imports; however, domestic producers argue this is insufficient to level the playing field.
- Recent Export Restrictions: China recently tightened its graphite export policies, further constraining supply to the U.S. and exacerbating concerns over resource accessibility.
Industry Perspectives:
- Domestic Producers: U.S. graphite miners contend that the proposed 920% tariff is necessary to mitigate China’s market dominance and to encourage investment in domestic graphite mining and processing capabilities.
- Automotive Manufacturers: Some automakers express apprehension that such a steep tariff could escalate production costs, potentially making EVs less affordable and hindering the industry’s growth.
Government Actions:
- Policy Considerations: The U.S. Department of Commerce and the International Trade Commission are currently evaluating the petition. Their decision will weigh the benefits of protecting domestic industries against the potential for increased costs to consumers and manufacturers.
- Strategic Initiatives: This development aligns with broader U.S. efforts to reduce dependence on foreign sources for critical minerals, thereby enhancing national security and supply chain resilience.
Implications:
- Supply Chain Dynamics: If approved, the tariff could incentivize the development of domestic graphite mining projects, reducing reliance on Chinese imports. However, it may also lead to short-term supply shortages and increased costs for industries reliant on graphite.
- Global Trade Relations: The proposed tariff represents a significant escalation in trade tensions between the U.S. and China, particularly concerning critical minerals vital to emerging technologies and renewable energy solutions.
Conclusion:
The petition for a 920% tariff on Chinese graphite imports underscores the strategic importance of this mineral in the evolving energy landscape. As the U.S. seeks to strengthen its domestic supply chains for critical materials, policymakers must balance the interests of domestic producers, manufacturers, and consumers in an increasingly complex global trade environment.