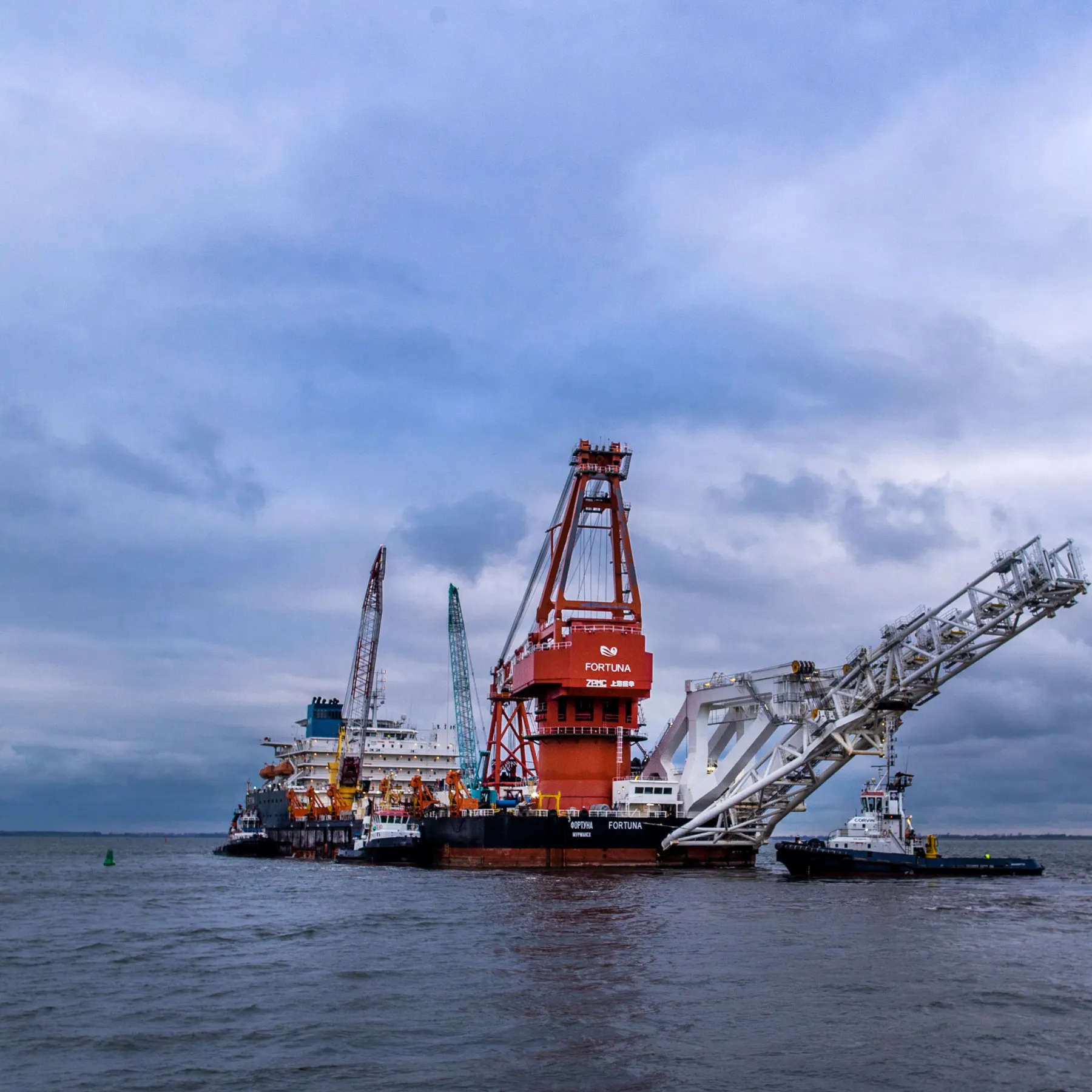
On December 18, 2024, the United States announced an expanded set of sanctions targeting entities involved with the Nord Stream 2 pipeline. These sanctions mark a continued effort by the U.S. to counter Russian influence in Europe’s energy sector and to penalize its geopolitical maneuvers amid the ongoing war in Ukraine.
Key Details of the Sanctions
- Entities Sanctioned:
- Nord Stream 2 AG: The pipeline operator, already facing previous restrictions, is now subject to additional penalties.
- Russian Maritime Services: Specific companies providing technical and logistical support to Nord Stream 2 have been added to the sanctions list.
- Insurance Providers: A Russian-based insurer that supports companies involved in the pipeline’s maintenance and operation has also been targeted.
- Fleet Restrictions: Over a dozen vessels linked to the project, including those engaged in maintenance and repair, are now sanctioned, further crippling the pipeline’s operational capacity.
- Scope of Sanctions:
- These sanctions freeze the assets of targeted entities under U.S. jurisdiction.
- They prohibit transactions between sanctioned entities and U.S. citizens or companies, effectively cutting off these organizations from the American financial system.
U.S. Perspective
- Geopolitical Concerns:
- The U.S. views Nord Stream 2 as a strategic project designed by Russia to expand its influence over Europe’s energy markets. By bypassing Ukraine, the pipeline deprives Kyiv of crucial transit fees and weakens its geopolitical leverage.
- Deputy State Department spokesperson Vedant Patel emphasized that the sanctions aim to prevent Russia from leveraging energy exports to coerce or destabilize European nations.
- Support for Ukraine:
- The sanctions are part of a broader U.S. policy to support Ukraine in its defense against Russian aggression, ensuring that Moscow’s ability to fund its war efforts is constrained.
Background on Nord Stream 2
- Pipeline Overview:
- Nord Stream 2 was designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Germany via the Baltic Sea, doubling the capacity of the original Nord Stream pipeline.
- Completed in September 2021, the pipeline faced delays and operational suspension following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in early 2022.
- 2022 Damage Incident:
- In September 2022, sections of Nord Stream 1 and 2 were severely damaged in a series of underwater explosions. The U.S., UK, and Ukraine have denied Russia’s accusations of sabotage, while investigations into the incident are ongoing.
Implications of the Sanctions
- For Russia:
- These sanctions further isolate Russian energy projects from global markets, complicating Moscow’s efforts to monetize its vast natural gas reserves.
- The inability to rely on Western support, such as insurance and technical services, hampers Russia’s long-term energy infrastructure plans.
- For Europe:
- European nations, particularly Germany, have already shifted focus to reducing reliance on Russian gas by securing alternative supplies from the U.S., Qatar, and Norway. The expanded sanctions on Nord Stream 2 reinforce this trend.
- Countries like Poland and the Baltic states, which have long opposed Nord Stream 2, view the sanctions as a step toward enhancing Europe’s energy security.
- For Global Energy Markets:
- The sanctions may contribute to continued volatility in natural gas markets, particularly in Europe, where supplies are still stabilizing following the cessation of Russian gas imports.
Russia’s Response
- Accusations of Bias:
- Moscow has repeatedly accused the U.S. of exploiting the situation to promote its liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports to Europe.
- Russian officials have dismissed the sanctions as politically motivated and economically short-sighted.
- Domestic Adjustments:
- Russia is exploring partnerships with non-Western countries, particularly in Asia, to offset lost revenue from European markets.
Strategic Context
- U.S.-Russia Relations:
- The sanctions underscore the deepening rift between Washington and Moscow, with energy resources remaining a focal point of contention.
- Long-Term Energy Transition:
- While these sanctions aim to curb Russian influence, they also accelerate Europe’s transition to renewable energy sources and infrastructure for non-Russian gas imports.
Conclusion
The expanded sanctions on Nord Stream 2 are a testament to the geopolitical significance of energy in the ongoing conflict between Russia and the West. By targeting entities associated with the pipeline, the U.S. seeks to weaken Russia’s leverage while bolstering Europe’s energy independence. However, the broader implications for global energy markets and geopolitical stability remain uncertain as the situation continues to evolve.