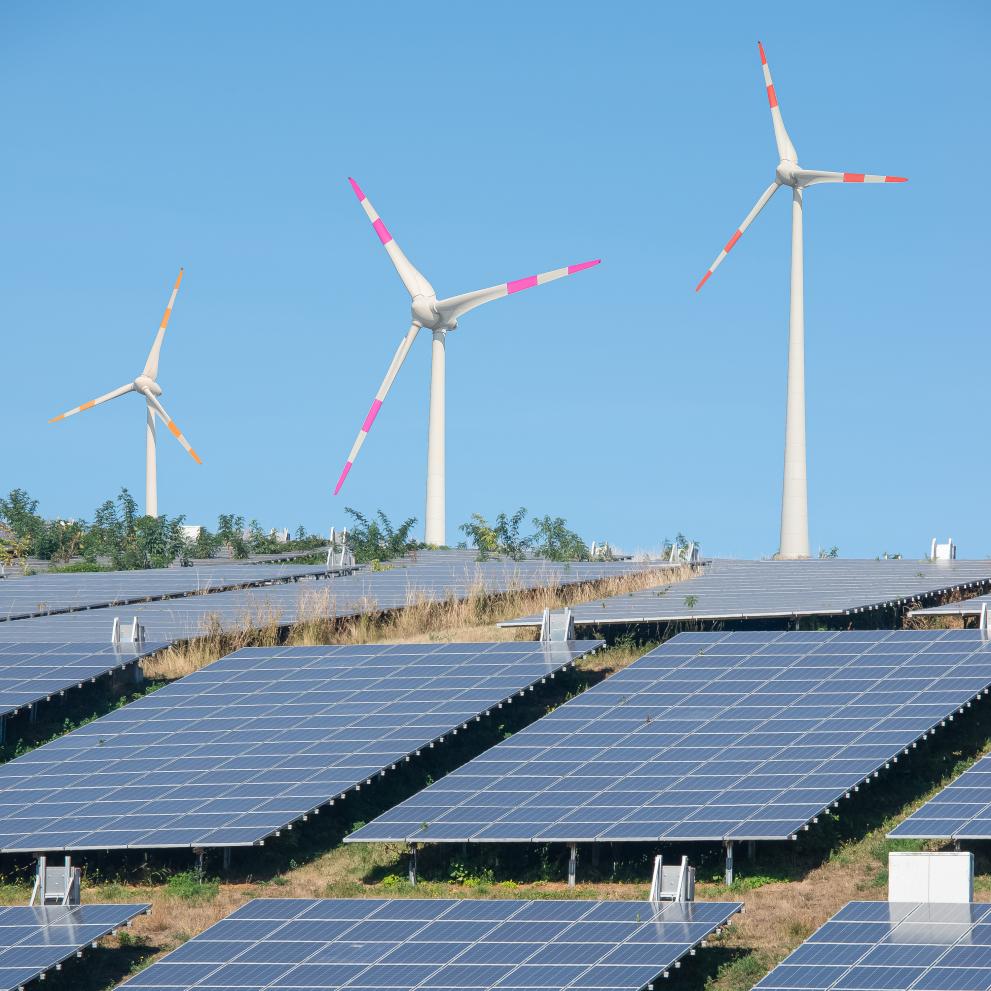
For the first time in history, solar energy has surpassed coal in electricity generation across the European Union, marking a major milestone in the region’s energy transition. The shift underscores Europe’s commitment to renewable energy and its efforts to reduce carbon emissions amid ongoing energy security challenges.
Key Findings
- Record-Breaking Solar Generation:
- Solar power accounted for a larger share of the EU’s electricity mix than coal in 2024, driven by record solar capacity installations and declining fossil fuel usage.
- Decline in Coal Usage:
- Coal-fired power plants have been progressively phased out due to stringent climate policies, rising carbon pricing, and the competitiveness of renewable energy alternatives.
- Energy Security Considerations:
- The EU has accelerated renewable energy deployment in response to geopolitical tensions and fossil fuel supply disruptions.
Driving Factors
- Policy and Regulatory Support:
- The EU’s Green Deal and national incentives have encouraged large-scale solar investments.
- Technological Advances:
- Improvements in solar panel efficiency and battery storage have increased solar’s reliability as a primary energy source.
- Cost Competitiveness:
- The levelized cost of solar energy continues to decline, making it more attractive than coal in most EU member states.
Implications for the Energy Market
- Reduced Carbon Emissions:
- A shift from coal to solar significantly lowers the EU’s carbon footprint, aligning with the bloc’s climate goals.
- Grid Modernization Needs:
- Increased solar penetration necessitates investments in smart grids and energy storage solutions to ensure stable electricity supply.
- Impact on Fossil Fuel Industries:
- Traditional coal-producing regions face economic transitions, requiring workforce reskilling and diversification strategies.
Challenges Ahead
- Intermittency Issues:
- Solar power generation fluctuates with weather conditions, necessitating improved energy storage solutions.
- Infrastructure Adaptation:
- The power grid must evolve to integrate high volumes of renewable energy effectively.
- Investment in Innovation:
- Continued funding in solar research and development is required to maintain growth and efficiency improvements.
Conclusion
The EU’s transition from coal to solar marks a significant step toward a sustainable energy future. While challenges remain, the trend highlights the growing viability of renewables as the backbone of the European electricity system. The continued expansion of solar energy, along with supportive policies and technological advancements, will be crucial in shaping the next phase of Europe’s energy landscape.
For more information, visit Semafor.