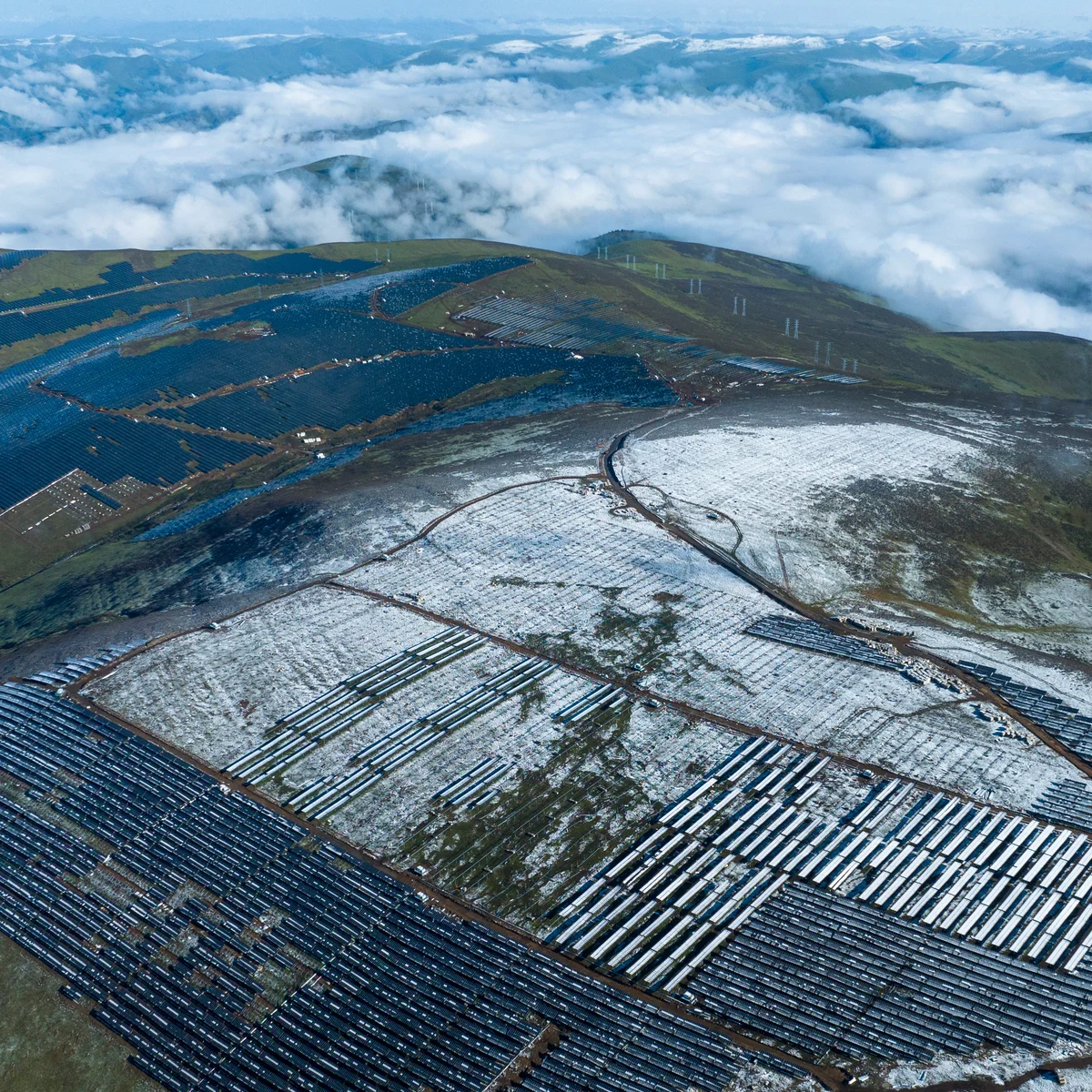
China is at the forefront of the global energy transition, with projections indicating that by 2028, half of its power will be sourced from low-carbon energy, including hydro, solar, wind, nuclear, and energy storage.
Renewable Energy Expansion
- Installed Capacity: By 2025, China’s combined solar and wind capacity is expected to surpass that of both Europe and North America.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Market Growth
- Market Share: Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) are projected to constitute about two-thirds of China’s passenger car sales by 2034, increasing to 89% when including hybrid electric vehicles.
- Production and Exports: China’s dominance in EV manufacturing has led to significant exports, impacting global markets, particularly in Europe.
Global Impact and Trade Relations
- European Union Response: The EU has imposed tariffs ranging from 7.8% to 45.3% on Chinese-built EVs to address concerns over market imbalances due to Chinese subsidies.
- Market Penetration: Chinese-brand EVs accounted for 27.2% of the EU market in the second quarter of 2024, up from 25.4% in the fourth quarter of 2023.
Challenges for Western Automakers
- Sales Decline: Companies like Tesla have experienced reduced sales in China, with a 4.3% year-on-year decrease in November 2024.
- Financial Write-downs: General Motors announced a write-down of up to $2.9 billion due to competitive pressures in the Chinese market.
Domestic Preferences
- Consumer Trends: Chinese consumers are increasingly favouring domestic EV brands such as BYD and Geely, attracted by their cost-effectiveness and technological advancements.
China’s strategic investments and policies have positioned it as a leader in the global shift towards renewable energy and electric mobility, influencing global markets and prompting policy responses from other major economies.